GIM Geobody
Introduction
The GIM Geobody seeks to construct a surface (Poly Data) that encloses some region of interest. In order to do so the user must first calculate a seismic attribute (see chapter: 12. Seismic Interpretation) so that the value of the seismic attribute inside the geobody is either larger than outside the geobody or the other way around.
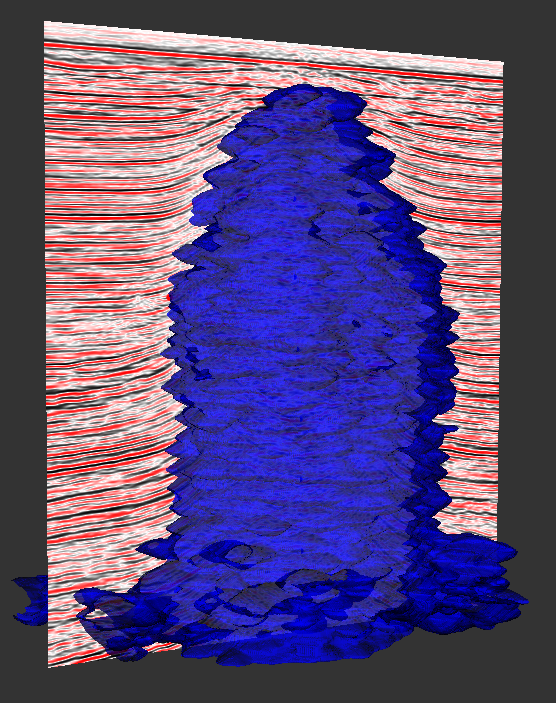
For instance in the case of a salt diapir one might use the Coherence attribute; the salt will have a smaller coherence than the region outside the salt.
In the case of a low amplitude channel one might use the Envelope attribute; the channel will have a lower envelope than the surrounding.
A geobody surface enclosing a salt diapir and its seismic. The Coherence attribute was used.
On this page:
Geobody Cube Contour
You are probably familiar with contours from maps. Here they are closed polygons going trough points on the map with the same elevation. In 3D contours becomes closed surfaces.
Since the value of the input seismic attribute inside the geobody is either lower or larger than outside the geobody; contouring on a value in between the values inside and outside the geobody will result in a surface describing the boundary.
As an example assume that the value is 0 inside the geobody and 1000 outside. Contouring on e.g. 500 will result in a surface describing the boundary.
The "Geobody Cube Contour" dialog is opened from:
GIM > GIM Analysis >Calculate Geobody Cube.
The Geobody Cube Contour dialog
Brick Cube
As input the "Geobody Cube Contour" takes a seismic attribute (Brick Cube).
Value
The other input is a value to contour on.
If you press down the pencil button; you can find the value in a sample in the brick cube by by left-clicking and pressing y. Press the pencil button again to exit read-off value mode.
Calculate volume
If the "Calculate volume" options is checked; the process will report the volume of all cells of the attribute cube that are completely within the geobody.
Connectivity Filter
A common problem with countouring is that there are regions outside the geobody that have the same attribute value as the geobody. To get rid of these regions you may select the value using the pencil button and check the "Connectivity filter" option.
Only regions that are connected to the point you clicked while selecting the value will then be included in the geobody.
Decimate
The resulting geobody surface is often very detailed. This makes it occupy a lot of memory and therefore take a long time to display. When the "Decimate" option is checked; the resulting surface will be simplified in a way that keeps the overall visual appearance.
As a result the decimated surface may take only 1/10 of the space of the undecimated surface, and therefore be much quicker to display, while looking almost similar to the undecimated surface. For how to smooth the result surface; see the Smooth Geobody chapter.
Resulting surface
The resulting surface is placed in a new top-level folder: Geobody, Geobody(1), ..., and named Contour.
Geobody Smoothing
The resulting surface from the Geobody Cube Contour process is often very detailed and this makes it appear "noisy". The solution is to smooth it afterwards.
The Geobody Smoothing dialog is opened from: GIM->Gim Analysis->Smooth Geobody.
The Geobody Smoothing dialog
The larger the Relaxation; the smoother the result will be. When increasing the Relaxation you should also increase Max Iterations so that the process do not become unstable.
The result is a surface named "Contour_Smooth" in the same folder as the input surface.
Geobody Calculation
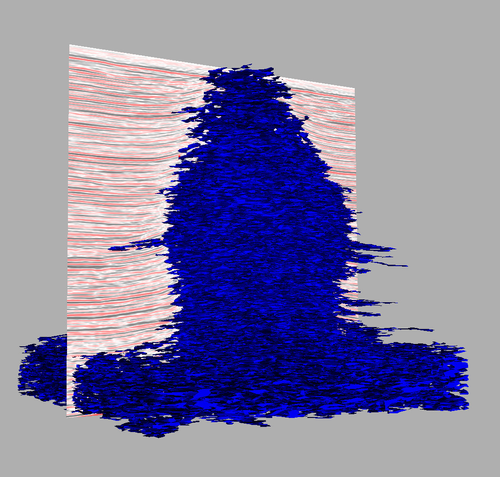
The image at the beginning of this chapter showed a nice and smooth geobody surface. The only problem is that applying the Geobody Cube Contour directly to the Coherence gives a let ideal result (even if using Connectivity filter):
The result of applying the Geobody Cube Contour directly to the Coherence attribute. Connectivity filter and Decimation was used.
We notice that there are regions outside the salt that are connected to the salt. Also the geobody surface have an huge amount of holes. Smoothing does not fix these problems.